The two main pillars of the Black Hole Mapper project are: i) time domain studies of quasars, and ii) large scale spectroscopic follow up of X-ray selected sources. This core is complemented by a small number of supplementary BHM programs, which increase the scientific grasp of the project.
BHM Time-Domain Programs
The BHM optical (BOSS) repeat spectral time-domain programs emphasize the astrophysics of quasars, including studies of BH masses, binarity, accretion and events, broad line region (BLR) dynamics, outflows, etc., requiring spectral sampling at a broad range of timescales/cadence, ranging from days to decades; this is achieved via the AQMES and RM programs.
| Tier | No. of ~15 min BOSS exposures per epoch (mag limits) | Approx no. of epochs to be obtained | Approx. no. of fields | Approx. total no. of targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQMES WIDE | 4 (i<19.1) | ~1-2 | ~400-600 (mainly North) | ~20,000 |
| AQMES MEDIUM | 4 (i<19.1) | ~10 | ~35-60 (mainly North) | ~2000 |
| RM | 8 (i<~21) | ~100 | ~4 (North+ South) | ~1000 |
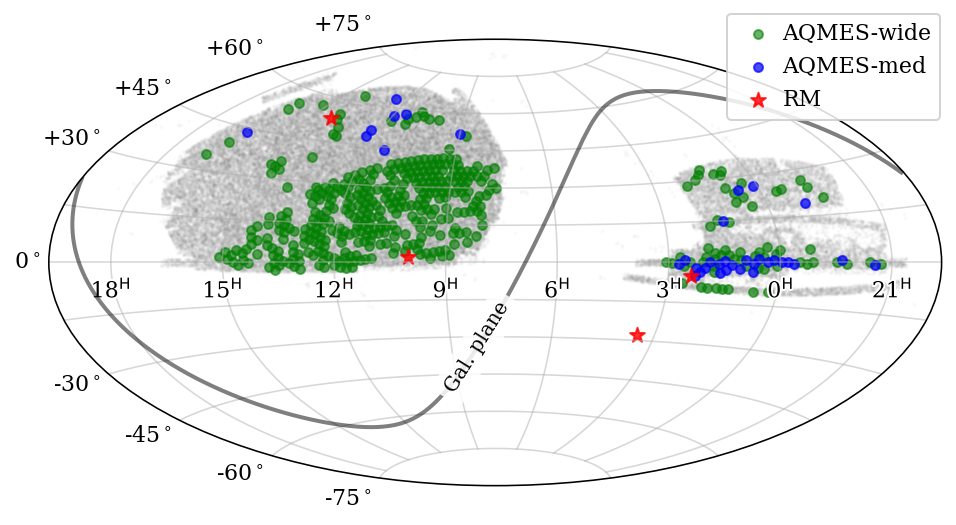
AQMES (All-Quasar Multi-Epoch Spectroscopy)
The AQMES core program includes both a wide-area and low-cadence tier, and a modest-area and modest cadence tier, adding new epochs in SDSS-V to quasars/AGN also with at least one previous epoch of SDSS I to IV spectra, e.g., selected mainly from the DR16 quasar catalog (Lyke et al., 2020)
- AQMES-Wide: For ~20,000 quasars, at least one more epoch will be added during SDSS-V, and combined with earlier-epoch SDSS spectra, sampling ~1-10 yr timescales, e.g., to probe the BLR dynamics of the most massive BHs, statistics of changing look quasars, broad absorption line (BAL) disappearance/emergence, etc. (this is a wide area, but low-cadence time-domain tier; ~2000 deg2).
- AQMES–Medium: For ~2000 quasars, ~10 epochs added in SDSS-V, probing down to ~1-month to 1-year timescales, adding unfolding BLR structural and dynamical changes (a medium tier in area and cadence; ~200 deg2).
In addition, we will repeatedly observe fainter QSOs within the dedicated AQMES-Wide and AQMES-Medium fields, as well as opportunistically targeting known QSOs outside of that area, where fiber-resources permit.
For more details please see the dedicated AQMES page.
RM (Reverberation Mapping)
- Reverberation Mapping (RM; another core BHM program) aims — for ~103 quasars in 4 dedicated fields — to obtain optical (BOSS) repeat spectra with a high-cadence of >102 epochs, sampling down to days to weeks. The lags between the continuum and BLR emission yield BH masses, advancing RM measures to a broad range of luminosity and redshift (a small area, but high-cadence tier; ~30 deg2).
For more details please see the dedicated Reverberation Mapping page.
BHM X-ray Follow-up Programs
BHM optical (BOSS) spectroscopic follow-up of X-ray sources include a large core program (SPIDERS) relying on eROSITA X-ray data , and a more modest program relying on Chandra archival X-ray data.
SPIDERS (SPectroscopic IDentfication of ERosita Sources)
The main goal of the core SPIDERS program is to provide a complete and homogeneous optical spectroscopic followup of X-ray sources (both point-like and extended) detected by eROSITA (in ~ 10,000 deg2 at high-Galactic latitude, within the German or ‘DE’ half of the sky). SPIDERS uses X-ray data from eROSITA’s first 1.5 years of operation, which began in 2019 (emphasizing eFEDS mini-survey spectroscopic follow-up in DR18, and eRASS (all-sky) follow-up data later in SDSS-V).
- The wide area component of SPIDERS utilizes data through eRASS:3 (first 3 eROSITA all-sky scans), and aims to obtain the optical spectroscopic identifications and redshifts, evolution, and astrophysics of ~300,000 X-ray source counterparts, especially AGN (but also including ~104 X-ray emitting clusters of galaxies).
- The SPIDERS/eFEDS program (beginning in SDSS-IV and completed in the first year of SDSS-V operations) collected BOSS spectroscopy for ~104 candidate counterparts, located within a 140 deg2 region of the sky that was observed by eROSITA as part of its performance verification phase. The SDSS-V optical spectra of eFEDS targets formed a centerpiece of the DR18 data release. See Aydar et al., (2025) for more details.
The core samples of SPIDERS targets rely on optical counterparts selected from the DESI Legacy Surveys catalogues. In order to complete the sky coverage ( particularly towards lower Galactic latitudes) the core program is supplemented by additional SPIDERS targets selected via optical imaging surveys including Pan-STARRS, Gaia, SkyMapper and SuperCosmos.
| Component | No. of ~15 min BOSS exposures per epoch (mag limits) | Approx no. of epochs to be obtained | Approx. no. of fields | Approx. total no. of targets |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPIDERS (main) | 3-4 (i<21.5) | ~1 | ~600 (N) + ~2800 (S) | >250,000 |
| eFEDS | ~4 (i<21.5) | ~1 | 37 (equatorial) | >10,000 |
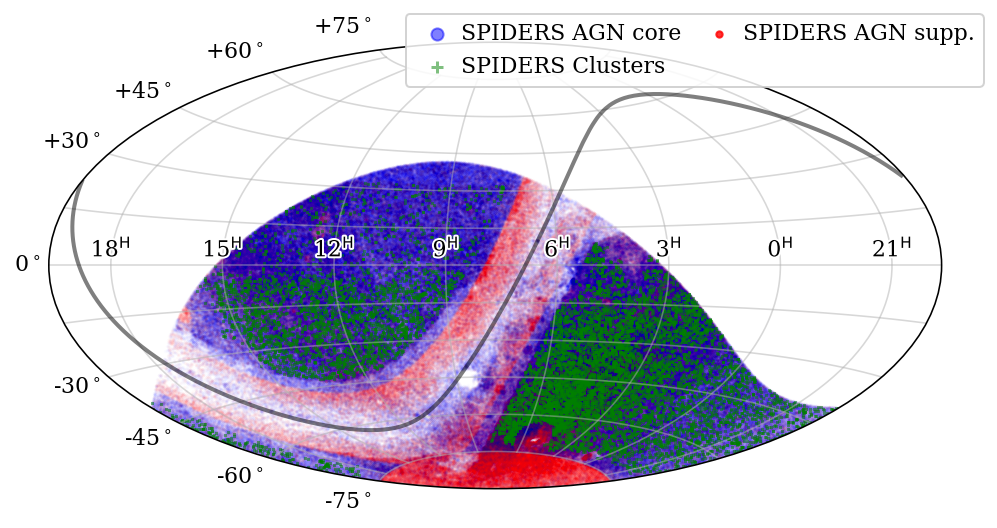
For more details please see the dedicated SPIDERS page.
CSC (Chandra Source Catalog)
A related, more modest, program of mainly optical (BOSS) spectroscopy of X-ray counterparts (but including some IR APOGEE spectra as well), involves tens of thousands of X-ray source counterparts selected from the Chandra Source Catalog.
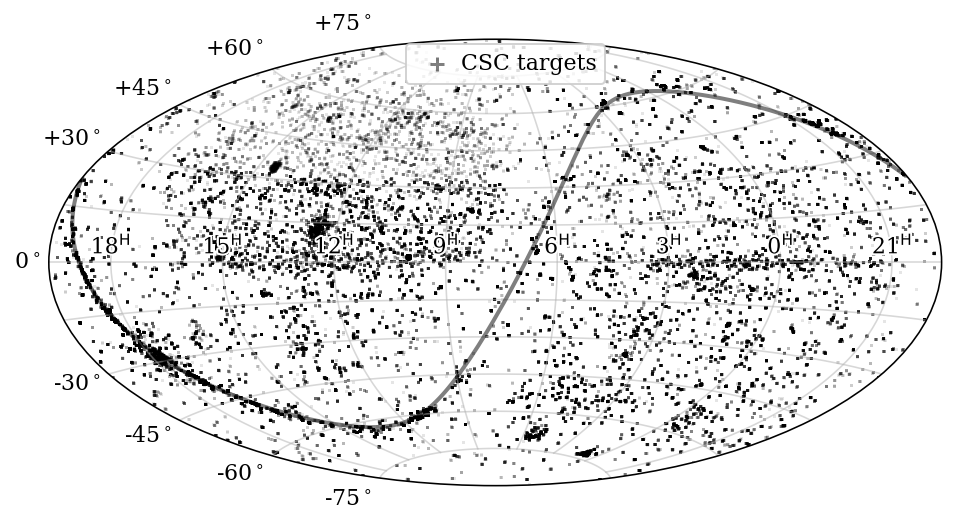
For more details please see the dedicated CSC page.
BHM Ancillary programs
In order to usefully use spare BOSS fiber-hours, the BHM team have devised two lower priority filler programs, targeting i) optical/IR selected QSOs and ii) bright low redshift galaxies. In addition, a number of programs within the SDSS-V openfiber framework are targeting samples of AGN/QSOs.
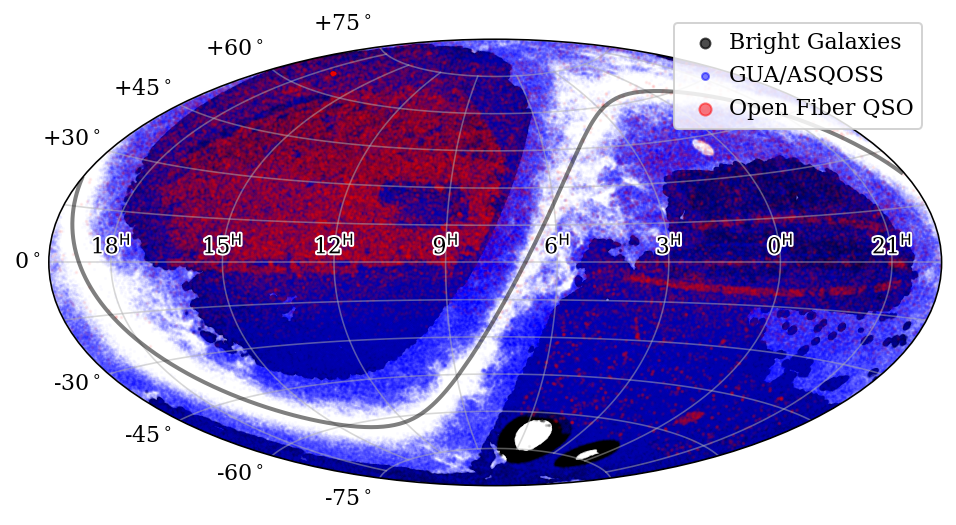
For more details please see the dedicated BHM Ancillary Programs page.
